Trading Terminology
Forex
Forex stands for FOReign EXchange. Forex is also known as forex trading, currency trading, foreign exchange market or FX. It is an international trading system for the exchange of major and minor currencies, i.e. the foreign exchange market, whose mid-range courses are considered
as official world courses.
Lot
Lot is a measurement that we use in forex trading. One lot equals one hundred thousand units. So if we buy 1 lot in EURUSD, our investment is worth $100,000. If you go long 1 lot on EURUSD, one pip equals $10 of price fluctuation. Because EURUSD can move fifty to a hundred pips a day, this can be a lot for traders with smaller accounts.
Because of that, brokers allow opening positions smaller than 1 lot, namely:
- A mini lot, which is ten thousand units.
- A micro lot, which is one thousand units.
- A nano lot, which is a hundred units.
Leverage
The principle of leverage is using a small amount of equity supplemented by substantially larger amounts of foreign capital to finance the investment. This practice can magnify profits but also losses. Leverage is, therefore, a tool that increases the size of the maximum position that you can open as a trader.
For a better understanding, let’s give an example:
- Suppose a trader has a balance of $1,000 in his account, and his broker provides a leverage of 1:500. $1,000 * 500 would be equal to a maximum size of $500,000 per position. In other words, the trader can trade orders 500 times greater than the deposit. And this is the basic pillar of understanding leverage. If leverage 1:500 is utilized, the trader will earn $500 instead of $1 for the same investment. Of course, it is important to emphasize that losses can be equally rapid.
Margin
The required amount of funds needed to participate in the market.
Trading on margin with leverage is a process in which a broker allows a trader to borrow money (either from a broker or from an investment bank) and purchase a particular instrument. Margin is the difference between the total value of an investment and the amount provided to the trader.
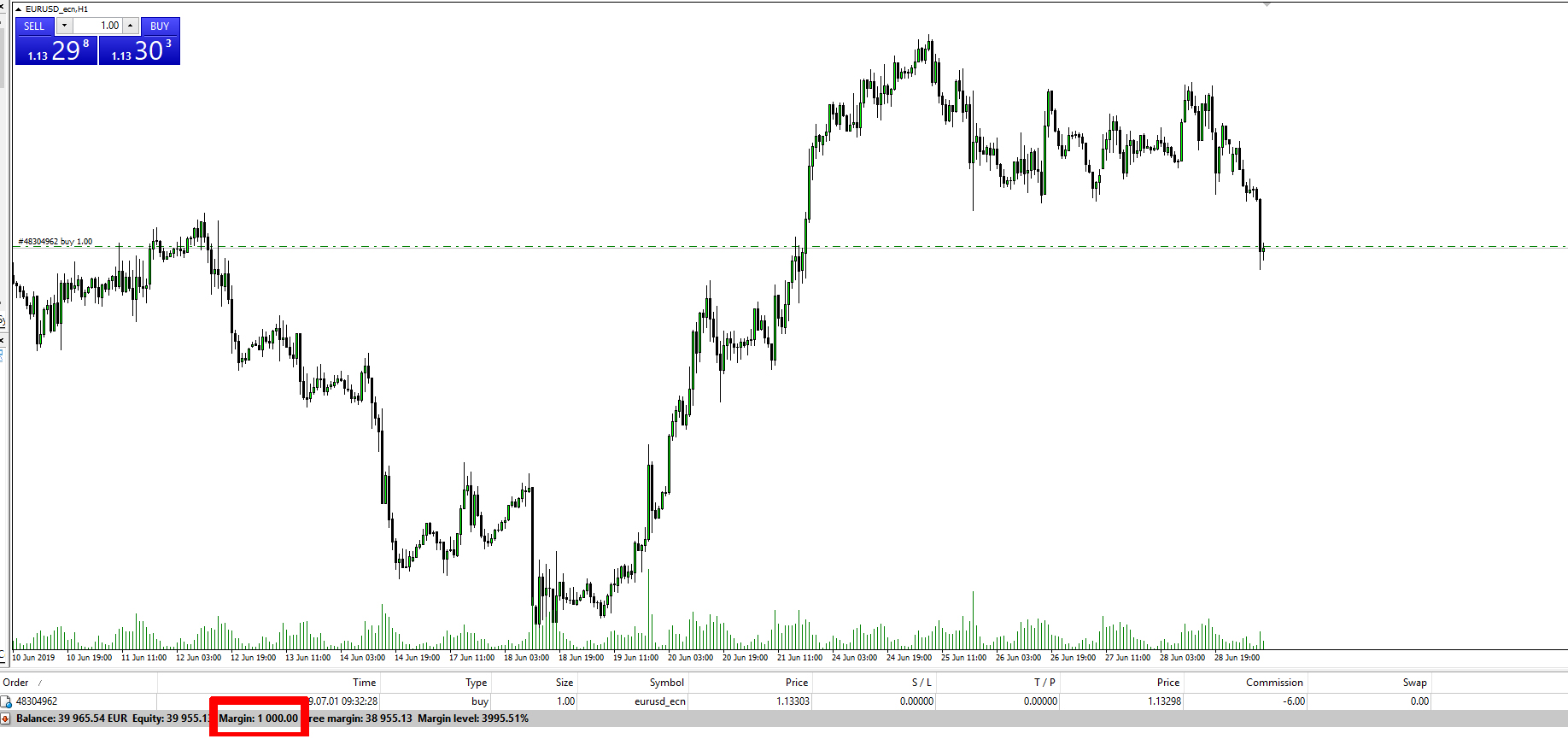
Let’s take a look at a practical example on the platform:
- When we open 1 lot of EURUSD pair, the margin is what we must hold on the trading account. For this example, when the leverage is 1:100, it is a minimum of $1,000.
Hedging
In finance, the notion of hedging means creating a position in a particular market to minimize risk from another position. There are many different tools through which you can hedge. Some examples are insurance contracts, forwards, swaps, options, many different over-the-counter derivatives, and arguably the most popular are futures contracts.
Futures exchanges arose in the 18th century to allow transparent, standardized and effective hedging against the movement of prices of agricultural commodities.
Pip
Currency pairs increase or decrease by the value traditionally measured in the so-called PIPs (Price Interest Point, or Points in Percentage). PIP is defined as a “percentage of one percent”, or 0.01%.
Traditionally, forex prices have been quoted in a certain number of decimal places – more often to four decimal places – and initially, the PIP was moving by one point in the last decimal place. Most brokers now dimension forex instruments in one extra decimal place, which means that PIP is no longer the last decimal place.
The exceptions you’ll notice include currency pairs with a Japanese yen – for these pairs, one pip value is the second decimal place, while the price mostly has three decimals.
We’ll give you an example:
Let’s say you buy a currency pair EURUSD for 1.11510 and later, you close your position at 1.11520. The difference between the two prices is: 1.11510-1.11520 = 0.00010-in other words, the difference is just one PIP. The price of the financial instrument is always stated in two values:
Bid
The bid represents the price of demand – i.e. the price for which the contract can be sold at a given moment.
Ask
Ask represents the price of the offer – i.e. the best price at which the contract can be purchased at the moment. The retail trader, therefore, always gets a less advantageous price.
Spread
The difference between supply (ask) and demand (bid) is called a spread. It is, therefore, the difference between the price claimed by the seller of the instrument and the price at which the buyer is willing to buy. The spread is the expense that a trader must consider while trading.
Trading strategy
The absolute necessity for every trader is the so-called trading strategy.
Each trader has his own financial objectives and acceptable level of risk, which influences the choice of the financial instrument that he/she buys or sells, as well as the settings of input and output limits, profit with stop loss, and analysis of a possible market direction.
All these factors combined set a specific trading strategy and give a trader an edge. This edge is an important part of any trading strategy. If a trader does not have an edge, then he/she hardly achieves favourable results in his/her trading.
Volatility
Volatility indicates the fluctuations in the value of an asset or its rate of return over a given period of time and expresses the risk of investing in an asset. Volatility is an essential heartbeat for a trader because it moves the price of the instrument up and down. When the volatility is zero, the trader cannot make any profit or loss.
Trading approach
The trading approach is the same as a trading strategy. It differs for every trader.
Scalpers
This is probably the hardest one you can pick. Why?
Scalpers are in and out of the markets very quickly; their trades last from minutes to sometimes just a few seconds. Because of that, you are required to focus 100% during the whole trading session. Scalpers also miss a lot of trading opportunities and rely solely on the big winner they are able to catch once in a while. This is something that can be very demanding on your psychology as you lose a lot and no one likes losing. So why do people choose to be scalpers if it is so hard?
There are two major reasons for that.
The first one is the returns. Being in and out of the market means you are getting many opportunities in the market every day. Swing traders, for example, have to wait several days for the right opportunity and they quite often sit at their hands and wait.
Scalpers do the exact opposite. Even though their win rate is usually lower, they can easily compensate for it with the reward to risk ratio and the number of opportunities they get.
The second reason, which is not often talked about, is freedom. Scalpers and day traders, whom we are going to talk about next, don’t really care about long term movements in the market. Because of that, they trade during their currently active session, which can be 4, 8, or 10 hours long. Once they are done, they don’t have to care about the market until their next trading session. This reduces the stress of babysitting any long-term positions which could disrupt your sleep and generally stress you out.
Day traders
Day traders are similar to scalpers in a lot of things.
They also watch markets in their predetermined sessions, but usually, they want to watch the market the whole day. They are not interested in quickly being in and out of the trades, but they much rather capture a bigger intraday move. For that reason, they only open a handful of positions, yet sometimes they even stay flat for a whole day. Although day traders are required to watch the market for longer, the approach tends to be more relaxed with high focus only required when the market trades around their desired level.
Day traders usually hold trades for a few hours. As they try to capture the bigger moves, they know they have to give the market room to breathe. They generally do not hold positions overnight, but sometimes they do as they try to capture even bigger intra-week moves.
Swing traders
Swing traders are looking to capture intra-week moves. They hold positions for a couple of days, sometimes weeks. Swing trading is very popular among beginner traders because it doesn’t require much chart time and analysis. You can prepare for your trades in the morning and thanks to alerts and limit orders, you let the market do its thing with very low input.
This sounds like a piece of cake, right? Are there any downfalls?
Yes, there are. Swing trading requires an extreme amount of patience as you often have to wait for several days for the market to give you your desired setup. And the real work begins once you enter the position. Because you are holding the position for a longer time, you must be ready for swings in price and sometimes disrupted sleep. Also, since you are taking fewer trades, building your track record will take much longer.
Position traders
You will hardly become a position trader early in your trading career. Position traders are also called investors. They hold their trades for weeks, months, or years and they usually follow large fundamental sentiments. A big amount of capital is required to become a position trader.
Broker
A brokerage firm is a legal entity that provides its customers with access to the capital market, thus acting as a necessary third party for buying and selling securities. It facilitates secure transactions on behalf of its customer, who executes their own trades on his/her trading account.
A Forex broker is a company registered in the commercial register dealing with the mediation of access to trading on financial markets, especially in forex. The broker company generates profits by charging spreads and trading commissions.
Forex broker provides its customers with the trading platform (software for access to financial markets), monitors current market events, issues, and opinions, and communicates ideas for trading in the form of comments, fundamental or technical analysis, etc.
When choosing a forex broker, paying attention to market capitalization, company history, number of active clients, registration, license, and security of finances is recommended.
Limit/Market orders
When you place a market order, you are going to get filled immediately at the best available price. One of the biggest problems with market orders is the risk of slippage during high-impact news and the fact that you always pay the spread.
On the other hand, the limit order says that you only want to get in the market at one desired price and nothing else. Limit orders are considered a patient approach, their disadvantage is the fact that traders might get too patient and miss their desired fill.
Stop Loss/Take Profit
Stop Loss and Take Profit are very straightforward. Stop Loss gets traders out of a trade when it goes against them. Traders place Stop Losses at various technical levels or fixed-point values. Using a Stop Loss prevents traders from unexpected spikes in price, which could result in significant losses.
Take Profit is in the same order as Stop Loss but on the opposite side. Take Profit gets traders out of a winning trade at a predetermined price.
Reward to risk ratio – RRR
The reward to risk ratio is very simple. It is how much you risk compared to how much you can gain.
If you risk $100 to gain $300, your reward to risk ratio is three to one. If you are risking $100 and you have a fixed $100 reward, you need to be right over 50% of the time to be profitable. With two to one reward to risk ratio, you only need to be right 40% of times to make money. The higher reward to risk ratio you have, less the percentage strike rate you need to be a profitable trader.
The equity simulator on our website is a great tool you can use to show the expectancy of your trading based on strike rate and reward to risk ratio.
Trading sessions
There are three major trading sessions in trading forex:
- Asian
- European
- North American
All of these sessions provide opportunities in the different markets as the volume changes throughout the day. If you are trading an Asian session, trading a pair like EURGBP doesn’t make much sense. But looking at AUDJPY should bring great trading opportunities.
The European and North American sessions have the highest volume, and markets are moving across the board in these sessions.



